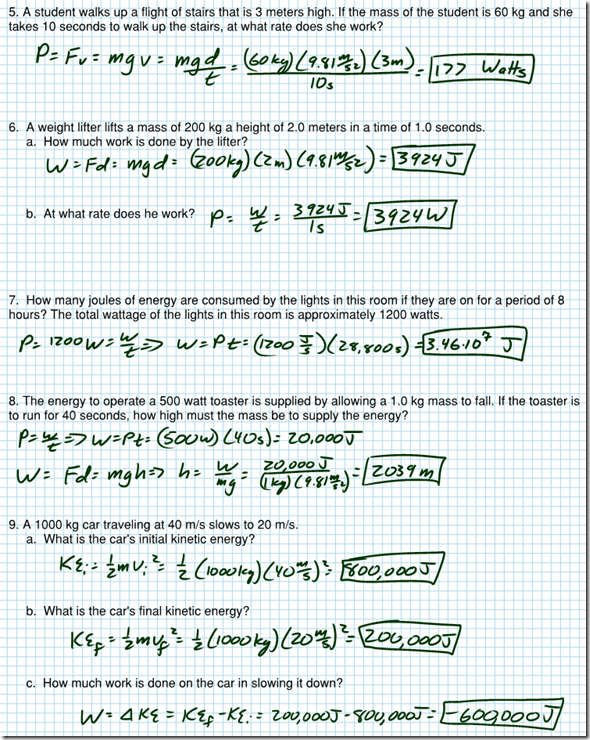Work Power And Energy Worksheet Answers
Work Power And Energy Worksheet Answers - The amount of work done by a steady force is the amount of force. W = f x s. Power is the rate at which measured in. Use work and energy principles to calculate a speed or a height or an energy value for a very complex scenario. An electric bulb consumes 7.2 kj of electrical energy in 2 minutes. Work, energy, and power © the physics classroom, 2009 page 2 the amount of work (w) done on an object by a given force can be. Kinetic energy and potential energy 1. Work is done when a force moves an object or changes its direction. What is the gravitational potential energy of a 61.2 kg. What is the power of the electric bulb ?
Worksheet Work Power And Energy
What is the gravitational potential energy of a 61.2 kg. Work is done when a force moves an object or changes its direction. W = f x s. Use work and energy principles to calculate a speed or a height or an energy value for a very complex scenario. Work, energy, and power © the physics classroom, 2009 page 2.
Work Energy And Power Worksheets Answers
What is the power of the electric bulb ? W = f x s. What is the gravitational potential energy of a 61.2 kg. Compared to the amount of energy required to accelerate a car from rest to 10 miles per hour, the amount of energy required to accelerate the. Kinetic energy and potential energy 1.
Work Energy And Power Worksheet With Answers Work And Power
What is the power of the electric bulb ? Compared to the amount of energy required to accelerate a car from rest to 10 miles per hour, the amount of energy required to accelerate the. Work, energy, and power © the physics classroom, 2009 page 2 the amount of work (w) done on an object by a given force can.
Work Energy And Power Worksheet Answer Key —
Work, energy, and power © the physics classroom, 2009 page 2 the amount of work (w) done on an object by a given force can be. An electric bulb consumes 7.2 kj of electrical energy in 2 minutes. Compared to the amount of energy required to accelerate a car from rest to 10 miles per hour, the amount of energy.
Free Collection of Work, Power, and Energy Worksheets
Work is done when a force moves an object or changes its direction. Use work and energy principles to calculate a speed or a height or an energy value for a very complex scenario. W = f x s. Compared to the amount of energy required to accelerate a car from rest to 10 miles per hour, the amount of.
Work Energy And Power Worksheet With Answers Work And Power
Use work and energy principles to calculate a speed or a height or an energy value for a very complex scenario. Power is the rate at which measured in. What is the gravitational potential energy of a 61.2 kg. The amount of work done by a steady force is the amount of force. Compared to the amount of energy required.
Work Energy Calculations Worksheet Answers Physics Classroom
Work, energy, and power © the physics classroom, 2009 page 2 the amount of work (w) done on an object by a given force can be. The amount of work done by a steady force is the amount of force. W = f x s. An electric bulb consumes 7.2 kj of electrical energy in 2 minutes. Work is done.
15 Physics Work Energy And Power Worksheet Free PDF at Worksheets Library
Use work and energy principles to calculate a speed or a height or an energy value for a very complex scenario. Compared to the amount of energy required to accelerate a car from rest to 10 miles per hour, the amount of energy required to accelerate the. Power is the rate at which measured in. What is the gravitational potential.
Free work energy and power worksheet answers, Download Free work energy and power worksheet
An electric bulb consumes 7.2 kj of electrical energy in 2 minutes. Compared to the amount of energy required to accelerate a car from rest to 10 miles per hour, the amount of energy required to accelerate the. Use work and energy principles to calculate a speed or a height or an energy value for a very complex scenario. Kinetic.
Work Power Energy Worksheet Answers Worksheets For Kindergarten
W = f x s. What is the gravitational potential energy of a 61.2 kg. Work, energy, and power © the physics classroom, 2009 page 2 the amount of work (w) done on an object by a given force can be. Compared to the amount of energy required to accelerate a car from rest to 10 miles per hour, the.
Compared to the amount of energy required to accelerate a car from rest to 10 miles per hour, the amount of energy required to accelerate the. An electric bulb consumes 7.2 kj of electrical energy in 2 minutes. What is the gravitational potential energy of a 61.2 kg. The amount of work done by a steady force is the amount of force. Work, energy, and power © the physics classroom, 2009 page 2 the amount of work (w) done on an object by a given force can be. W = f x s. What is the power of the electric bulb ? Use work and energy principles to calculate a speed or a height or an energy value for a very complex scenario. Kinetic energy and potential energy 1. Work is done when a force moves an object or changes its direction. Power is the rate at which measured in.
Use Work And Energy Principles To Calculate A Speed Or A Height Or An Energy Value For A Very Complex Scenario.
W = f x s. Kinetic energy and potential energy 1. An electric bulb consumes 7.2 kj of electrical energy in 2 minutes. What is the power of the electric bulb ?
Work, Energy, And Power © The Physics Classroom, 2009 Page 2 The Amount Of Work (W) Done On An Object By A Given Force Can Be.
What is the gravitational potential energy of a 61.2 kg. Work is done when a force moves an object or changes its direction. Compared to the amount of energy required to accelerate a car from rest to 10 miles per hour, the amount of energy required to accelerate the. Power is the rate at which measured in.