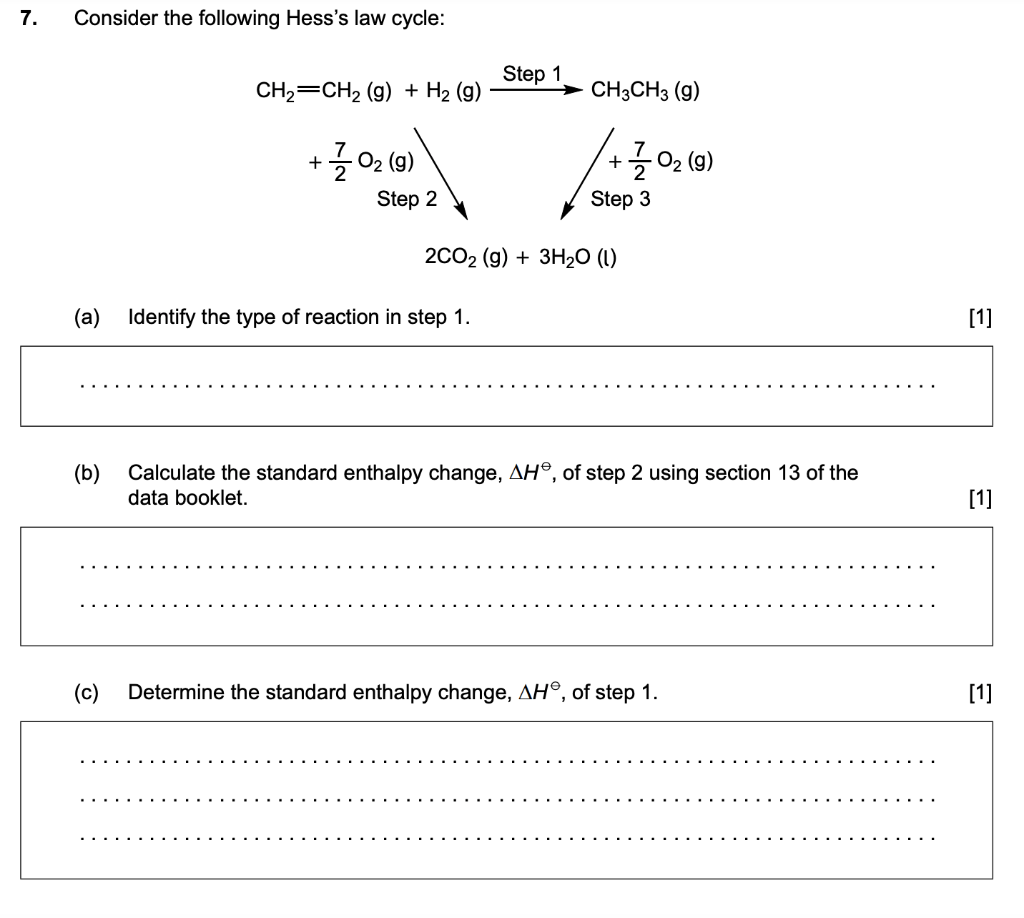
Hess's Law Worksheet
Hess's Law Worksheet - C2h4 (g) + h2 (g) → c2h6 (g), from the following data. Refer to the table of heats of formation for the individual step. Complete these questions using the additivity of heats method. Chem 12 hess’s law worksheet 1. Hess's law worksheet ‐ answers 1. C2h4 (g) + 3 o2 (g) à 2. C2h4 (g) + h2 (g) à c2h6 (g), from the following data: C2h4 (g) + 3 o2 (g) → 2 co2 (g) + 2 h2o (l) ∆h = ‐1411. Calculate ∆h for the reaction: Hess's law worksheet calculate h for the reaction:
Hess Law A Level Chemistry Questions
Calculate the δh for the reaction: Chem 12 hess’s law worksheet 1. C2h4 (g) + 3 o2 (g) → 2 co2 (g) + 2 h2o (l) ∆h = ‐1411. Hess's law worksheet calculate h for the reaction: Refer to the table of heats of formation for the individual step.
Chemistry Practice Hess’s Law Problems by Teach Simple
Calculate the δh for the reaction: C2h4 (g) + h2 (g) → c2h6 (g), from the following data. Hess's law worksheet ‐ answers 1. C2h4 (g) + 3 o2 (g) → 2 co2 (g) + 2 h2o (l) ∆h = ‐1411. C2h4 (g) + 3 o2 (g) à 2.
Hess's Law Worksheet 8 General chemistry CH 221 Docsity
Calculate ∆h for the reaction: Refer to the table of heats of formation for the individual step. C2h4 (g) + h2 (g) à c2h6 (g), from the following data: Hess's law worksheet calculate h for the reaction: C2h4 (g) + 3 o2 (g) à 2.
Chemistry Practice Hess’s Law Problems by Teach Simple
C2h4 (g) + 3 o2 (g) → 2 co2 (g) + 2 h2o (l) ∆h = ‐1411. Hess's law worksheet ‐ answers 1. Refer to the table of heats of formation for the individual step. Chem 12 hess’s law worksheet 1. C2h4 (g) + h2 (g) à c2h6 (g), from the following data:
Hess Law 1 Chemsheets
Calculate ∆h for the reaction: Refer to the table of heats of formation for the individual step. Complete these questions using the additivity of heats method. C2h4 (g) + 3 o2 (g) → 2 co2 (g) + 2 h2o (l) ∆h = ‐1411. C2h4 (g) + h2 (g) → c2h6 (g), from the following data.
WorksheetHess Law with Answer Key Exercises Chemistry Docsity Worksheets Library
C2h4 (g) + 3 o2 (g) → 2 co2 (g) + 2 h2o (l) ∆h = ‐1411. Calculate ∆h for the reaction: Calculate the δh for the reaction: Complete these questions using the additivity of heats method. Hess's law worksheet calculate h for the reaction:
Ap Chemistry Hess's Law Worksheet
Calculate the δh for the reaction: Chem 12 hess’s law worksheet 1. Refer to the table of heats of formation for the individual step. Calculate ∆h for the reaction: Hess's law worksheet ‐ answers 1.
30++ Hess's Law Worksheet Answers Worksheets Decoomo
Hess's law worksheet ‐ answers 1. C2h4 (g) + h2 (g) à c2h6 (g), from the following data: C2h4 (g) + h2 (g) → c2h6 (g), from the following data. Hess's law worksheet calculate h for the reaction: Calculate the δh for the reaction:
Solved CHEM 12 Hess's Law Worksheet 1. Calculate the AH for
Refer to the table of heats of formation for the individual step. C2h4 (g) + h2 (g) → c2h6 (g), from the following data. C2h4 (g) + h2 (g) à c2h6 (g), from the following data: Complete these questions using the additivity of heats method. Hess's law worksheet ‐ answers 1.
Hess's Law Worksheet
Refer to the table of heats of formation for the individual step. C2h4 (g) + h2 (g) → c2h6 (g), from the following data. Calculate the δh for the reaction: C2h4 (g) + 3 o2 (g) → 2 co2 (g) + 2 h2o (l) ∆h = ‐1411. Chem 12 hess’s law worksheet 1.
Calculate the δh for the reaction: Complete these questions using the additivity of heats method. Hess's law worksheet calculate h for the reaction: Calculate ∆h for the reaction: Refer to the table of heats of formation for the individual step. C2h4 (g) + 3 o2 (g) à 2. C2h4 (g) + 3 o2 (g) → 2 co2 (g) + 2 h2o (l) ∆h = ‐1411. C2h4 (g) + h2 (g) à c2h6 (g), from the following data: Hess's law worksheet ‐ answers 1. C2h4 (g) + h2 (g) → c2h6 (g), from the following data. Chem 12 hess’s law worksheet 1.
Complete These Questions Using The Additivity Of Heats Method.
C2h4 (g) + h2 (g) à c2h6 (g), from the following data: Hess's law worksheet calculate h for the reaction: Refer to the table of heats of formation for the individual step. C2h4 (g) + 3 o2 (g) à 2.
C2H4 (G) + 3 O2 (G) → 2 Co2 (G) + 2 H2O (L) ∆H = ‐1411.
Calculate ∆h for the reaction: C2h4 (g) + h2 (g) → c2h6 (g), from the following data. Calculate the δh for the reaction: Chem 12 hess’s law worksheet 1.